Obstacle Avoiding Robot using Arduino

Introduction of Obstacle Avoiding Robot
Obstacle Avoiding Robot is an intelligent device which can automatically sense the obstacle in front of it and avoid them by turning itself in another direction. This design allows the robot to navigate in unknown environment by avoiding collisions, which is a primary requirement for any autonomous mobile robot. The application of Obstacle Avoiding robot is not limited and it is used in most of the military organization now which helps carry out many risky jobs that cannot be done by any soldiers.
Here an Ultrasonic sensor is used to sense the obstacles in the path by calculating the distance between the robot and obstacle. If robot finds any obstacle it changes the direction and continue moving.
Components Required
1. Arduino NANO or Uno (any version)
2. HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
3. LM298N Motor Driver Module
4. 5V DC Motors
5. Battery
6. Wheels
7. Chassis
8. Jumper Wires
Code for Obstacle Avoiding Robot
/* Obstacle Avoiding Robot Using Ultrasonic Sensor and Arduino
* Iotian Hub(www.iotianhub.com)
*/
int trigPin = 9; // trig pin of HC-SR04
int echoPin = 10; // Echo pin of HC-SR04
int revleft = 4; //Reverse motion of Left motor
int revright = 6; //Reverse motion of Right motor
int fwdleft = 5; //Forward motion of Left motor
int fwdright = 7; //Forward motion of Right motor
long duration, distance;
void setup() {
delay(random(500,2000)); // delay for random time
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(revleft, OUTPUT); // set Motor pins as output
pinMode(fwdleft, OUTPUT);
pinMode(revright, OUTPUT);
pinMode(fwdright, OUTPUT);
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT); // set trig pin as output
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT); //set echo pin as input to capture reflected waves
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH); // send waves for 10 us
delayMicroseconds(10);
duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH); // receive reflected waves
distance = duration / 58.2; // convert to distance
delay(10); // If you dont get proper movements of your robot then alter the pin numbers
if (distance > 19)
{
digitalWrite(fwdright, HIGH); // move forward
digitalWrite(revright, LOW);
digitalWrite(fwdleft, HIGH);
digitalWrite(revleft, LOW);
}
if (distance < 18)
{
digitalWrite(fwdright, LOW); //Stop
digitalWrite(revright, LOW);
digitalWrite(fwdleft, LOW);
digitalWrite(revleft, LOW);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(fwdright, LOW); //move backword
digitalWrite(revright, HIGH);
digitalWrite(fwdleft, LOW);
digitalWrite(revleft, HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(fwdright, LOW); //Stop
digitalWrite(revright, LOW);
digitalWrite(fwdleft, LOW);
digitalWrite(revleft, LOW);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(fwdright, HIGH);
digitalWrite(revright, LOW);
digitalWrite(revleft, LOW);
digitalWrite(fwdleft, LOW);
delay(500);
}
}
Applications
· Obstacle avoiding robots can be used in almost all mobile robot navigation systems.
· They can be used for household work like automatic vacuum cleaning.
· They can also be used in dangerous environments, where human penetration could be fatal.
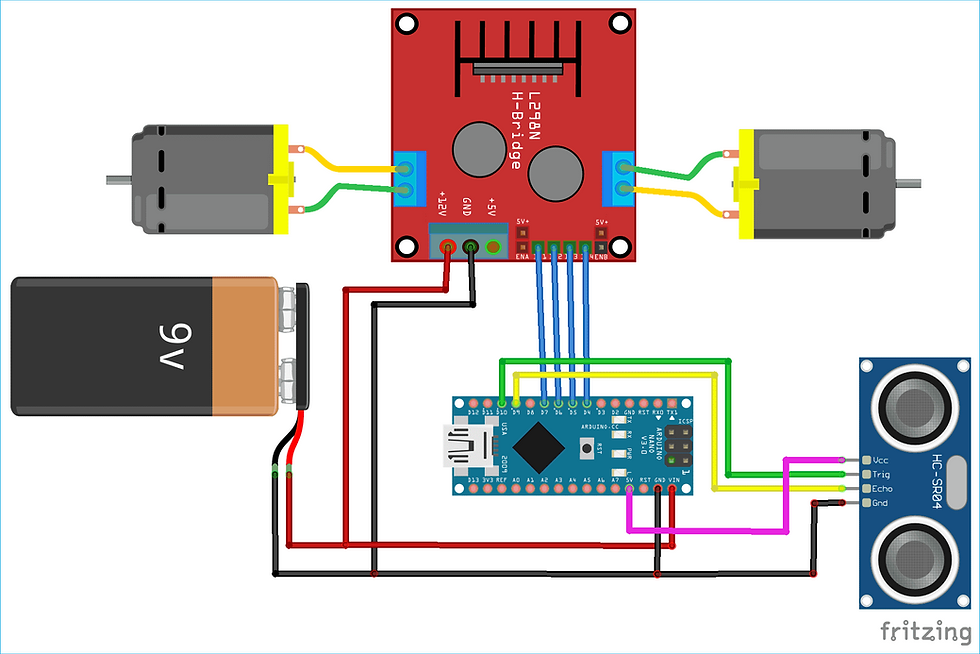
Figure 1
