Wifi Controlled Robot using Arduino
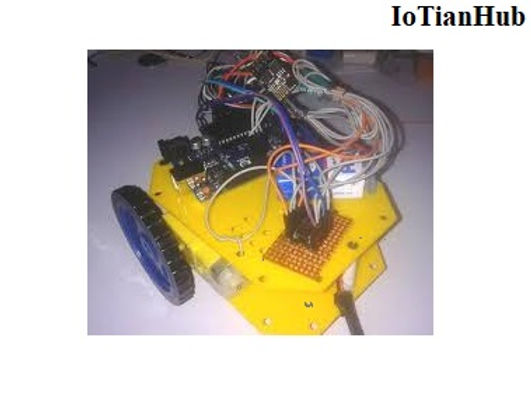
Introduction
And now we are adding one more Robot in our ‘Robotics Projects’ section, this time we are going to make a Wi-Fi controlled Robot using Arduino and Blynk App. This Arduino based Robot can be controlled wirelessly using any Wi-Fi enabled Android smart phone.
For Wi-Fi Controlled Robot we have used Blynk android app. It is very simple app for the Arduino, to make IoT based project. This app can easily downloaded from the Google Play Store, and also can be easily configured.
Steps for Blynk application setup
-
First download it from Google Play Store and install it in Android mobile phone.
-
After this, it is required to create an account. You may use your current Gmail account.
-
Now select Arduino Board and give a name for your project.
-
Note down the Auth Token Code or simply mail it to your Email Account and then copy and paste in Arduino sketch (Program Code)
-
Enter this Auth Token Code in Arduino sketch.
-
Then click on create button in Blynk app.
-
Now Select the Joystick Widget, Click on Joystick, Configure the Joystick.
-
After it press Play button at the right top of screen.
Required Component
-
Arduino UNO
-
ESP8266 Wi-Fi Module
-
USB Cable
-
Connecting wires
-
L293D
-
DC Motors
-
Batteries
-
10K POT (optional)
-
Robot chassis plus wheel
-
Roller caster
-
Android Mobile phone
-
Blynk App
Circuit Diagram(See in figure 1)
We mainly need a Arduino and ESP8266 Wi-Fi module. ESP8266’s Vcc and GND pins are directly connected to 3.3V and GND of Arduino and CH_PD is also connected with 3.3V. Tx and Rx pins of ESP8266 are directly connected to pin 2 and 3 of Arduino. Software Serial Library is used to allow serial communication on pin 2 and 3 of Arduino.
A L293D Motor Driver IC is used for driving DC motors. Input pins of motor driver IC is directly connected to pin 8, 9, 10 and 11 of Arduino. And DC motors are connected at its output pins. Here we have used 9 Volt battery for driving the Circuit and DC motors.
Working(See in figure 2)
Working of the Wi-Fi controlled Robot is very easy, we just need to Drag or Slide the Joystick in the direction, where we want to move the Robot.
-
if we want to move the Robot in Forward direction then we need to Drag the Joystick ‘circle’ in Forward direction.
-
we can move the Robot in Left, Right and Backward direction by Dragging the joystick in respective direction.
-
Now as soon as we release the Joystick, it will come back to center and Robot stops.
Blynk App sends values from Two Axis Joystick to Arduino, through Wi-Fi medium. Arduino receive the values, compare them with predefined values and move the Robot accordingly in that direction.
Code
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial // Comment this out to disable prints and save space
#include <ESP8266_SoftSer.h>
#include <BlynkSimpleShieldEsp8266_SoftSer.h>
// Set ESP8266 Serial object
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial EspSerial(2, 3); // RX, TX
ESP8266 wifi(EspSerial);
// You should get Auth Token in the Blynk App.
// Go to the Project Settings (nut icon).
char auth[] = "caa17a11c0124d4083d0eaa995f45917";
#define m11 8
#define m12 9
#define m21 10
#define m22 11
void forward()
{
digitalWrite(m11, HIGH);
digitalWrite(m12,LOW);
digitalWrite(m21,HIGH);
digitalWrite(m22,LOW);
}
void backward()
{
digitalWrite(m11, LOW);
digitalWrite(m12,HIGH);
digitalWrite(m21,LOW);
digitalWrite(m22,HIGH);
}
void right()
{
digitalWrite(m11, HIGH);
digitalWrite(m12,LOW);
digitalWrite(m21,LOW);
digitalWrite(m22,LOW);
}
void left()
{
digitalWrite(m11, LOW);
digitalWrite(m12,LOW);
digitalWrite(m21,HIGH);
digitalWrite(m22,LOW);
}
void Stop()
{
digitalWrite(m11, LOW);
digitalWrite(m12,LOW);
digitalWrite(m21,LOW);
digitalWrite(m22,LOW);
}
void setup()
{
// Set console baud rate
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(10);
// Set ESP8266 baud rate
// 9600 is recommended for Software Serial
EspSerial.begin(9600);
delay(10);
Blynk.begin(auth, wifi, "username", "password"); // wifi username and password
pinMode(m11, OUTPUT);
pinMode(m12, OUTPUT);
pinMode(m21, OUTPUT);
pinMode(m22, OUTPUT);
}
BLYNK_WRITE(V1)
{
int x = param[0].asInt();
int y = param[1].asInt();
// Do something with x and y
/* Serial.print("X = ");
Serial.print(x);
Serial.print("; Y = ");
Serial.println(y);*/
if(y>220)
forward();
else if(y<35)
backward();
else if(x>220)
right();
else if(x<35)
left();
else
Stop();
}
void loop()
{
Blynk.run();
}

Figure 1

Figure 2
